| Â Â Â serum: | ||
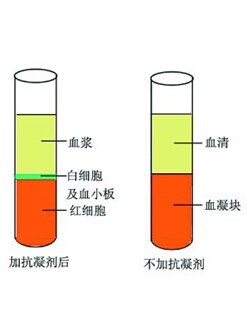
A pale yellow transparent liquid that is coagulated by blood. If the blood is taken out from the blood vessel and placed in a test tube without an anticoagulant, the blood coagulation reaction is activated, and the blood rapidly solidifies to form a jelly. The clot is contracted, and the pale yellow transparent liquid deposited around it is serum, which can also be obtained by centrifugation after coagulation. During the blood coagulation process, fibrinogen is converted into fibrin blocks, so there is no fibrinogen in the serum, which is the biggest difference from plasma. In the blood coagulation reaction, many substances are released from platelets, and each clotting factor also changes. These components are left in the serum and continue to change, such as prothrombin to thrombin, and gradually disappear or disappear with the serum storage time. These are also differences from plasma. However, a large number of substances that did not participate in the blood coagulation reaction were basically the same as plasma. In order to avoid the interference of anticoagulants, the analysis of many chemical components in the blood uses serum as a sample. | |||
   plasma: | |||
It is equivalent to the intercellular substance of connective tissue. It is an important component of blood and is a pale yellow liquid (because it contains bilirubin). Among the chemical components of plasma, water accounts for 90 to 92% , and solute is mainly plasma protein. Plasma protein is a general term for a variety of proteins, which can be divided into three categories: albumin, globulin and fibrinogen by salting out. The functions of plasma proteins are: maintaining plasma colloid osmotic pressure; composing a blood buffer system to participate in maintaining blood acid-base balance; transporting nutrients and metabolites, plasma proteins are hydrophilic colloids, and many insoluble substances are combined with them to become soluble. The substance in water; the nutritional function, the amino acid produced by the decomposition of plasma protein, can be used to synthesize tissue protein or oxidative decomposition to supply energy; participate in coagulation and immunity. The inorganic salts of plasma mainly exist in the ionic state, and the total amount of positive and negative ions is equal, maintaining electrical neutrality. These ions play an important role in maintaining plasma osmotic pressure, acid-base balance, and normal excitability of nerves and muscles. The various chemical components of plasma constantly change within a certain range. Among them, the concentrations of glucose, protein, fat and hormones are most susceptible to the nutritional status and the activity of the organism, while the concentration of inorganic salts is relatively small. The relatively constant physical and chemical properties of plasma is the primary manifestation of homeostasis. Plasma total osmotic pressure 313 milliosmoles per liter, equivalent to 7 atmospheres ( 5330 mm Hg, 1 mm Hg = 0.133 kPa), wherein the colloid osmotic pressure does not exceed 1.5 milliosmoles per liter ( 25 mm Hg) The rest is crystal osmotic pressure. pH 7.35 - 7.47 . The relative viscosity compared to water is 1.6 - 2.4 . | |||
Anticoagulant treatment of blood requires anticoagulant. What anticoagulant should be selected according to the specific experimental requirements. The blood consists of two components, the liquid component plasma and the formed hematopoietic cells, and the serum is a pale yellow clear liquid that precipitates after hemagglutination, and some coagulation factors and fibrinogen are less than plasma. Serum or anti-coagulant plasma is suitable for most biochemical tests. Most of the current serum samples are used. Preparation of serum samples without the addition of anticoagulant, release serum after placement can be analyzed, eliminating the preparation |
| ||
The step in which plasma must be centrifuged to separate blood cells from plasma. In addition, since the preparation of serum does not add anticoagulant, the anticoagulant is exempted from interference with some substances to be tested or their reaction systems. For example, oxalate can inhibit the activity of lactate dehydrogenase, acid phosphatase and amylase, and is not suitable. For the determination of calcium and potassium ( especially with potassium oxalate as an anticoagulant ) ; EDTA can inhibit the determination of alkaline phosphatase, angiotensin converting enzyme ( uric acid enzyme method ) ; fluoride interference with uric acid, urease determination, EDTA- The complexation of Na with calcium ions cannot be used for the determination of plasma calcium, sodium and nitrogen compounds; chelating anticoagulants are also banned by the inclusion of chlorine and calcium ions in the reaction system as determined by amylase. The above specimens may be anticoagulated with heparin. Some biochemical test items require rapid exchange of blood and cells between blood cells and plasma. It is necessary to separate blood cells and plasma as soon as possible after blood collection. This requires the addition of anticoagulant and timely delivery. Heparin is used as an anticoagulant to interfere with plasma components, but attention should be paid to the ratio of heparin activity unit to blood volume. The heparin concentration is generally 1000 units /ml . The heparin sterilizing solution of the above concentration is sucked with a syringe to wet the inner wall, and then the excess solution is discharged and used. After the blood is not taken from the heparin-free syringe, the blood should be quickly transferred to the heparin-containing test tube. It is best to use a dried heparin-containing tube to avoid dilution of the blood sample with a heparin solution. But heparin is more expensive. Obviously, heparin ammonia is not used for blood ammonia determination, and heparin sodium is not used for the determination of blood sodium. Plasma samples are suitable for the determination of ammonia, lactic acid, catecholamines, fibrinogen, plasma hemoglobin, and the like. For example, when blood cells are used as test specimens, for example, blood cell hormone receptor radioligand assay, erythrocyte nucleoside phosphorylase, various distinguishing nucleotides, creatine and the like are added to the anticoagulant to separate the hemorrhage cells for use. Anticoagulated whole blood specimens are rarely used directly for biochemical analysis, because it is often necessary to prepare a hemorrhagic filtrate for analysis. Especially after the clinical laboratory uses a fully automatic or semi-automatic biochemical analyzer, serum plasma specimens should be used for the experiment. | |||
We're professional Orthopedics Instruments manufacturers and suppliers in China, specialized in providing high quality medical instruments with reasonable price. We warmly welcome you to buy or wholesale bulk Orthopedics Instruments for sale here and get quotation from our factory.
Orthopedic Tools,Orthopedics Instruments,Orthopedic Surgical Instruments,Orthopedic Surgery Instruments
Tonglu WANHE Medical Instrument Co., Ltd , https://www.vanhurhealth.com