At present, it is a difficult job to diagnose potential patients with Alzheimer's disease (Alzheimer's disease). Recently, however, two scientists from South Korea claim that they use deep learning algorithms to diagnose patients with Alzheimer's disease in the next three years.
With the advent of the driverless and AlphaGo Master, artificial intelligence is expected to replace humans in most of the future. Recently, the medical diagnosis industry has come to the news that the deep learning neural network algorithm has surpassed the human doctor in the diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease.
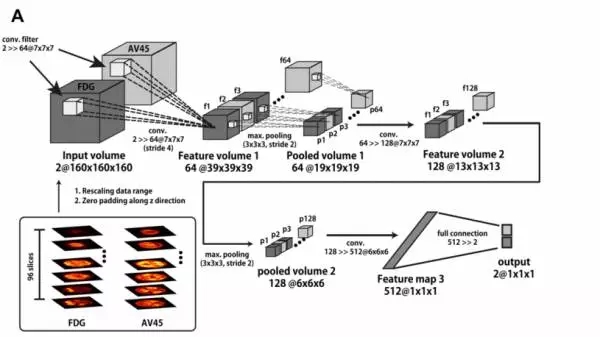
Alzheimer's disease, also known as Alzheimer's disease, is a chronic degenerative mental disorder and a common latent disorder in today's society. As we age, cognitive abilities are inevitably declining. We will become more forgetful, easier to forget our ideas, and more difficult to make decisions or complete tasks. Medically known as mild cognitive dysfunction, it is reflected in the process of aging in the vast majority of people.
Although some patients with mild cognitive impairment will not continue to worsen or even improve; however, many people with mild cognitive dysfunction will continue to aggravate their condition and become suffering from Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimer's patients can't express their wishes correctly, they will forget their relatives, lose their basic self-care ability, and ultimately rely on medical care workers. Many people have died a few years after their diagnosis.
In 2015, approximately 30 million people worldwide suffered from this disease. Due to the high cost, this condition places a heavy burden on the health care system worldwide.
Although there is currently no advanced method to delay the deterioration of this condition, it has been clinically shown that if diagnosed at an early stage, the patient's condition can be delayed or even controlled. Therefore, finding a reliable detection method to diagnose potential patients is critical to the patient's disease control. Doctors are eager to find patients who may have Alzheimer's disease early, because they will get the best results.
One current detection method is achieved by studying the positron emission map (PET) of the brain. The specific method is to detect the abnormal growth of amyloid plaques in the brain and the metabolic rate of glucose in the brain. Certain specific forms of PET scans can show signs of abnormality in both tests and serve as a basis for diagnosing whether mild cognitive impairment develops into Alzheimer's disease.
However, this is only clear in theory. In reality, reading PET is very difficult. Although researchers have found one or two significant criteria that can be used by professionally trained people, this approach is extremely time consuming and highly probable.
Hongyoon and Kyong replaced the current manual diagnosis with a deep learning algorithm. They said their algorithm could diagnose patients with Alzheimer's disease in the next three years and have a higher recognition rate.
Their implementation is very straightforward. In recent years, Alzheimer's researchers around the world have created a database of patient and non-patient brain scans. Both Hongyoon and Kyong use this database to train a neural network to identify differences between patients and non-patients.
The database contains normal brain scans of 182 70-year-old non-elderly dementia patients, as well as brain scans of 139 dementia patients of the same age. Using traditional training methods, artificial intelligence immediately learned how to distinguish between the two, and the accuracy rate is as high as 90%.
Later, Hongyoon and Kyong used the trained neural network to analyze another database. The database contains 181 70-year-old people with mild cognitive impairment, 79 of whom developed Alzheimer's disease three years later. The task of the algorithm is to identify these potential Alzheimer's patients.
The results of the experiment are very exciting. Hongyoon and Kyong said that the deep learning algorithm identified potential Alzheimer's patients with an accuracy rate of 81%. This accuracy is significantly higher than those who are trained. "These results indicate that it is feasible to use deep learning neural network algorithms combined with brain scan images to predict the occurrence of Alzheimer's disease."
This result demonstrates a rapid diagnosis of the underlying conditions of Alzheimer's disease, allowing potential patients to control the disease through early treatment, while also reducing the burden on the health care system, saving a lot of money.
At present, the application of deep learning in disease diagnosis is increasing, and Hongyoon and Kyong's technology is only one of them. The results of this experiment also show that deep learning is stronger than humans in the diagnosis of complex diseases. This technology can be used to detect a variety of conditions, from heart disease to cancer.
Obviously, the deep learning neural network algorithm will definitely lead to revolution in the medical field. Currently, for those with mild cognitive impairment, there is only a question of how long they will be ill.
Surgical Stapler Components,Suturing Device Guide Rod,Surgical Stapler Guide Rod,Suturing Device Screw
Changzhou Ziying Metal Products Co., Ltd , https://www.ziyingmetal.com