Recently, initiated by the Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province, the Institute of Radiology of Zhejiang University School of Medicine Shaoyifu Hospital Joint Medical Artificial Intelligence Alliance held the "Zhijiang Science Forum - Zhejiang University Medical College affiliated Shao Yifu Hospital 2018 Medical Imaging Summit Forum" Held at Shao Yifu Hospital.
At this forum, doctors and experts present not only discussed the clinical application of medical artificial intelligence, but also thought about the confusion that clinicians bring to the rapid development of artificial intelligence. During the meeting, Arterial Network interviewed three experts from Run Run Shaw Hospital to try to understand their application and thinking on the current status of medical AI.

Vice Chairman of Zhejiang CPPCC, Dean of Run Run Shaw Hospital, and famous surgical expert Cai Xiujun delivered the opening speech
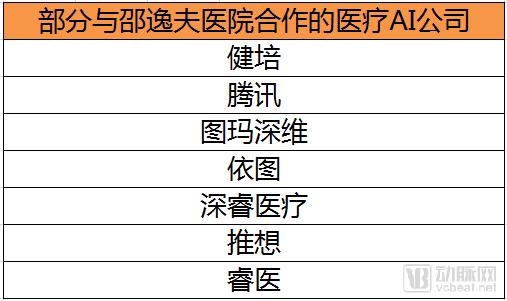
The products of 10 medical AI companies are all located at the Sir Run Shaw Hospital.
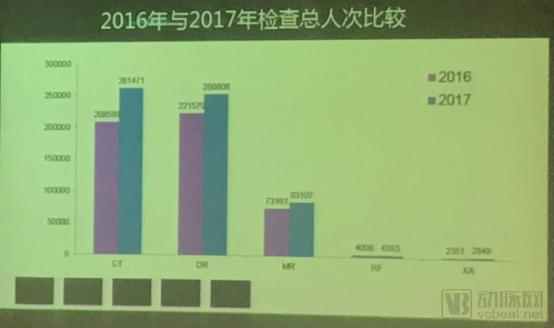
As a public top three hospital that passed the JCI International Hospital for four times, the inspection of the radiology department of the Run Run Shaw Hospital was amazing. According to Hu Hongjie, director of the radiology department, in 2017, the number of CT examinations in the hospital reached 261,471, the number of DR examinations reached 250,808, and the number of magnetic resonance examinations reached 83,107. Among them, the growth rate of CT and magnetic resonance examinations was as high as 25% and 13%, and the number of inspections in hospitals in the past five years was increasing at a double-digit rate.
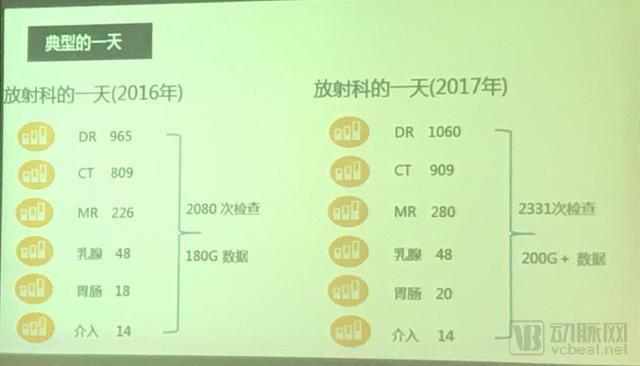
The heavy inspections bring a huge amount of work to the radiologist. In 2016, the hospital radiology department completed an average of 809 CT scans per day, and increased to 909 in 2017. According to Hu Hongjie, there will be an additional 100 people in 2018, more than 1,000.
As far as the current inspection volume is concerned, doctors can also issue reports on time. However, as the number of inspections continues to increase, manpower alone is not realistic. Therefore, it is necessary to use medical artificial intelligence to assist doctors to read films. Since 2016, 10 medical AI companies have cooperated with the Department of Radiology of the Run Run Shaw Hospital to polish medical AI products.
In these cooperative AI companies, the depth of cooperation varies. Some companies only put the products in the hospital for doctors to use, the effect is difficult to evaluate; some are installed in the hospital's PACS system with auxiliary diagnostic software, the doctor is relatively easy to use; the best way is that AI company arranges engineering personnel to the department Improve the product with the doctor.
Hu Hongjie said that at this stage, medical AI products are in the initial stage and are not enough to replace the doctor's work. Since medical treatment is an extremely complex process, medical AI can only assist in completing one of these steps, helping doctors in standardized, repeatable steps. For example, in the case of lung cancer screening, AI mainly bears the identification of lung nodules and the judgment of benign and malignant, while the doctor is responsible for finally considering whether the nodules need to be removed, as well as rehabilitation and life after surgery. "Although AI is still in its infancy, as a radiologist, to see the development of medical AI, it will change the workflow of existing doctors in the next few years." Hu Hongjie also said.

Chairman of the General Assembly, Professor Hu Hongjie, Director of Radiology, Run Run Shaw Hospital
In addition to the lungs, medical AI can also make a difference in other fields.
Although medical AI has developed rapidly, Hu Hongjie has also discovered some minor problems. For example, most AI companies cut in from lung nodule projects, and relatively few other areas of research and development. This situation is due to the huge amount of screening in the lungs. Take Shao Yifu Hospital as an example. For every 1000 CT examinations, 40% belong to chest CT, so the market space for lung nodule screening is very large.
However, we can't ignore that in addition to the screening of lung nodules, the screening of abnormal lesions such as thyroid nodules, breast nodules, liver occupying, prostate, etc. also requires a lot of labor, and the future needs are very large. . In order to improve these problems, in addition to directly using the products provided by the company to help them complete the polishing iteration, the hospital itself is also working with universities to develop medical AI products.
At present, there are three main aspects of the ongoing cross-disciplinary study between the Run Run Shaw Hospital and the university team:
1. Automatic grading around the liver's place
Liver occupancy grading is cumbersome, and the current mainstream approach is based on the LI-RADS standard promoted by the American College of Radiology. However, this standard system is constantly being updated, and many doctors do not have much time to learn to keep up with its updated rhythm.
Note: LI-RADS (Liver Imaging Reporting and Data System) was presented in March 2011 and has been widely used in clinical practice. The system is primarily intended for patients at risk for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and is designed to improve the reading, interpretation, and reporting criteria for liver CT and MRI. For high-risk groups of HCC, LI-RADS classifies liver nodules found by CT or MRI into five categories: benign, benign, and suspected HCC, HCC, HCC (LI-RADS 1-5, respectively) level).
Zhang Qiaoyu, deputy director of the Department of Radiology of the Sir Run Run Shaw Hospital, told the Arterial Network reporter that the department had cooperated with the computer department of Zhejiang University three years ago to solve this problem by using the AI ​​system for automatic grading.
At present, the comparison between the system developed by the Sir Run Run Shaw Hospital and the consistency of the two doctors found that the accuracy of the L-5 has reached 93.8%, while the doctor has only 92.3%.

Zhang Xiaoyu, deputy director of the Department of Radiology, Run Run Shaw Hospital
According to Zhang Qiaoyu, the development of medical AI products has now begun to affect the doctor's workflow. There are more and more doctors in the department who voluntarily choose to use medical AI products at work. In the past, the doctors' workflow was to write a report after reading the video. Now, before submitting the report, many doctors will choose to refer to the report issued by the AI ​​system, compare it with their own and check for missing vacancies. At some level, the AI ​​system can enhance the confidence of doctors in reporting.
However, Zhang Qiaoyi also said that the current stage of AI is AI, PACS is PACS, and the two have not fully realized seamless coordination . This makes the doctor seem to be not humanized during the operation, which will affect the enthusiasm of the doctor to some extent. Seamlessly connecting the AI ​​system to the PACS system will also be the next step in development.
2. Preoperative prediction of early recurrence of liver cancer based on imaging omics/machine learning method
According to Hu Hongjie, in the current clinical treatment of liver cancer, some relatively early liver cancer thought it could be cured well, but it relapsed during the rehabilitation process; some patients are already advanced, seemingly incurable, but recovered Very good.
There are some rules that doctors don't know yet. The hospital hopes to use the new generation of AI technology, its powerful computing power and learning ability to find this law. At present, the research has made some progress.
Tetanus Toxoid Vaccine,Toxoid Vaccine,Hep B Immune Globulin,Immunoglobulin Injections
FOSHAN PHARMA CO., LTD. , https://www.fospharma.com