Multicolor colonies are a common phenomenon encountered in microbiological testing. Colonies of different colors often represent different bacteria, and the classification and detection of multi-color colonies becomes an important task.
At present, the automatic classification of multi-color colonies is generally carried out by means of a colored cube. This method is simple to operate, but the effect is often not good. This is because:
(1) Each colony belonging to the same color has a surface color that is not exactly the same, and sometimes there are often considerable differences. For example, in the following figures 1-a and 1-b, the red colonies have deep red and light red, but obviously they belong to the same category; in Figure 1-c, the two red colonies are different in color and shade, and the surface is also caused by reflection. The color spots.
(2) For a single colony, the surface color is not constant, and the middle part is darker in color, while the other parts are slightly lighter in color, and there is even a lighter circle of color around the diffusion, as shown in Figure 1- Blue colonies in a.
For the above reasons, traditional methods such as colored cubes often divide a complete colony into many fragments. Figure 2 shows a partial enlargement of the segmentation of Figure 1 by this method. The pigmentation of blue colonies causes a colony to be divided into Inner and outer rings.
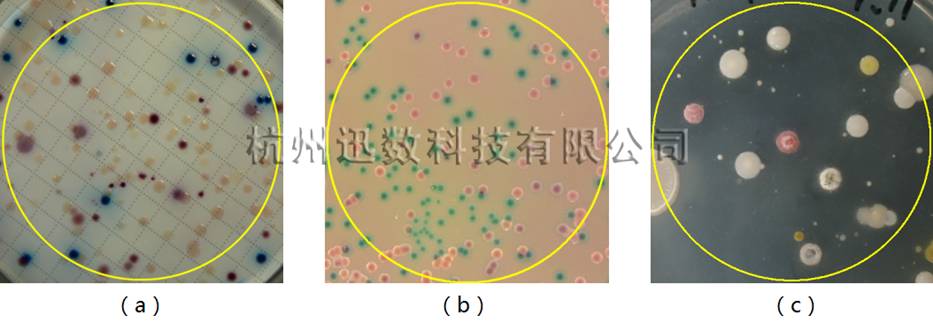
Figure 1 multicolor colony image

Figure 2 Over-segmentation due to uneven color (or diffusion) of colony surface
On the other hand, the image segmentation method based on the horizontal set active contour model has the advantages of strong anti-noise, good numerical solution stability, smooth and continuous segmentation, and does not cause over-segmentation or segmentation of many fragments. How to introduce color as a constraint condition into the horizontal set active contour model to solve the above-mentioned automatic classification of multi-color colonies is one of the goals of the rapid data research and development team in recent years. It has achieved success and can solve the problem of multi-color colony automatically. Classification problem.
1. Multi-color clustering of horizontal set active contour model based on RGB constraints
The basic principle of the horizontal set active contour model is to embed a curve or surface into a high-dimensional level set function, and use a high-dimensional function to express the evolution process of a low-dimensional curve or surface. Create a two-dimensional energy functional (ie CV model) with closed curve length and area smoothing constraints: 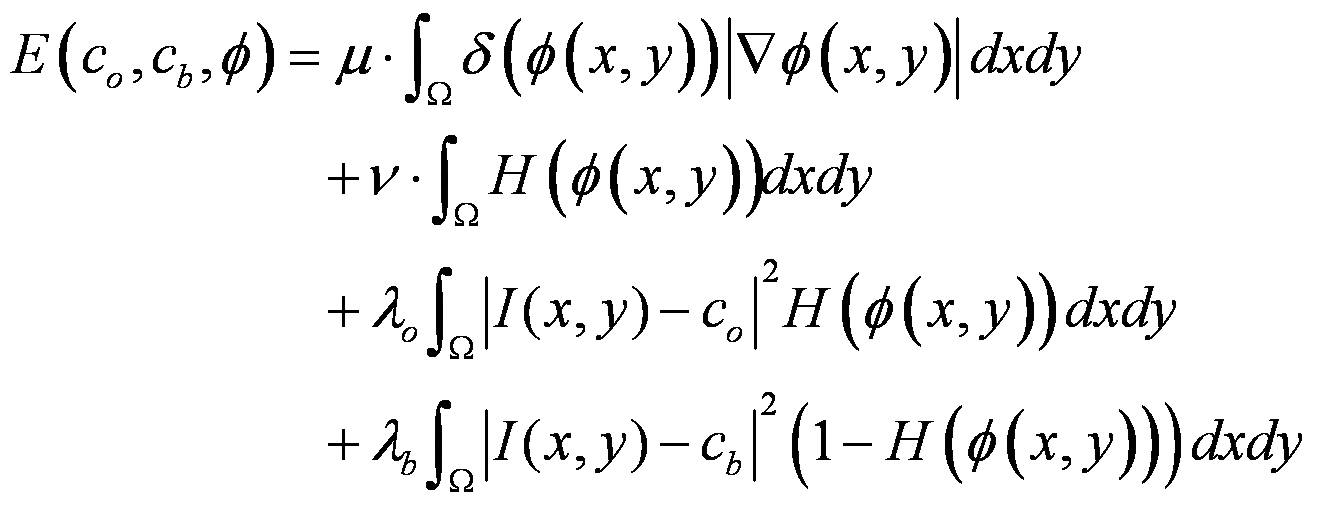
In the above formula, I ( x, y ) is the gradation of each pixel in the image, c o and c b are the average gradation values ​​inside and outside the colony outline, respectively. The first two of the above formula are used to control the smoothness of the colony contour curve, the latter two drive the contour to shrink to the actual colony contour, and the energy functional is minimized to complete the separation of the colony image.
The traditional CV model only uses gray scale information, and the multi-color colony rich in color information is low in efficiency. In order to incorporate color information therein, the conventional gray-scale information-based gradient indication function is changed to a color information-based gradient indication function. Let I ( x, y ) denote the three R , G , B vectors of the color image at the point ( x, y ). Define E , F , G, and f colors as follows:
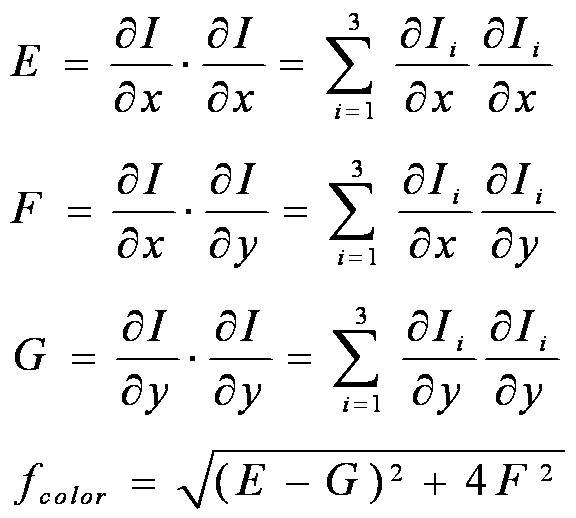
The energy function expression for E cv (Ф) is:
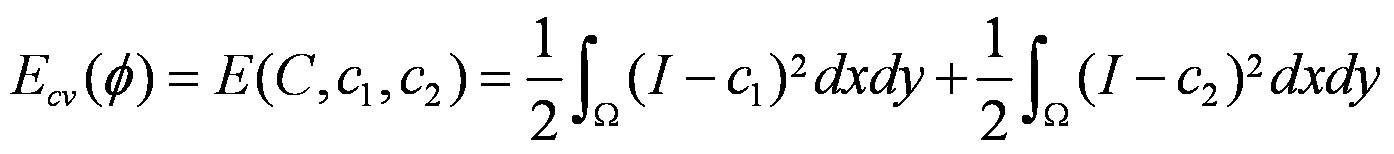
The gradient descent flow is as follows:
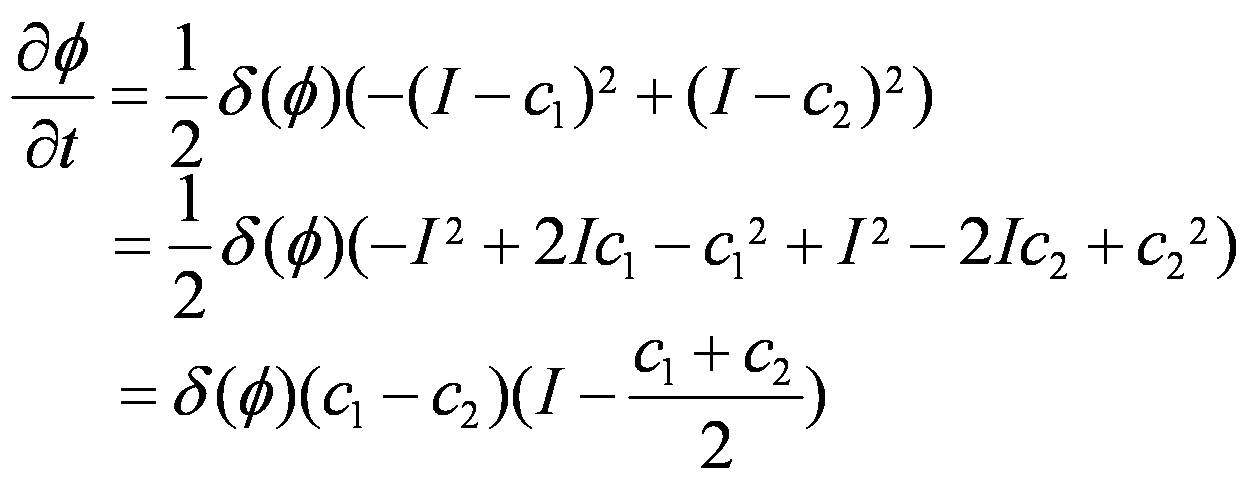
Wherein I, c 1, c 2 respectively is the image intensity, the average gradation value inside and outside contour. In order to add color information, the traditional gamma difference is changed to the weighted average of the difference of R , G , and B channels. The expression is as follows:
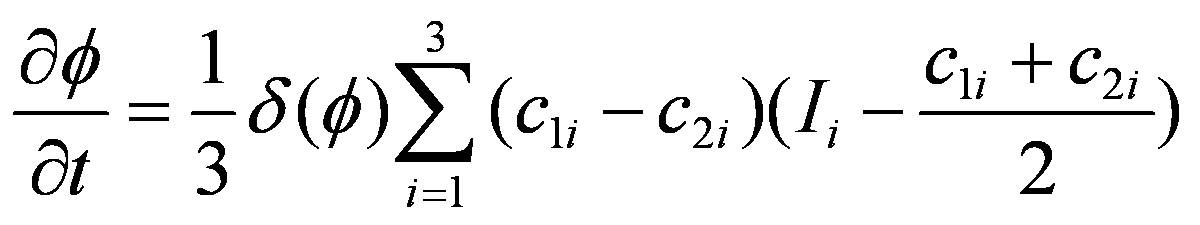
Where c 1i and c 2i are the average of the three channels inside and outside the contour line, and I i corresponds to the three channel intensity values. The curve evolution equations of the integrated color active contour model based on gradient and CV model are as follows:
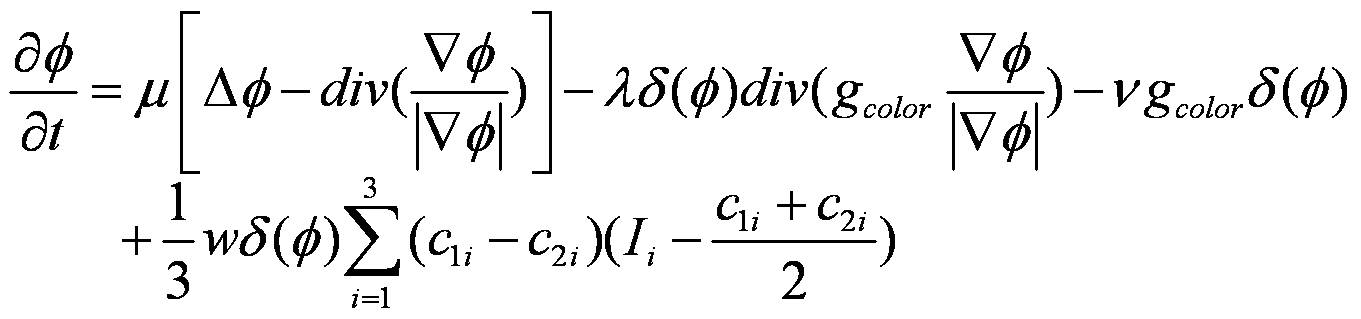
The above comprehensive active contour model based on color gradient and multi-channel CV model can better solve the problem of automatic color classification of multi-color colony images.
2 , automatic classification test of multi-color colonies
Figures 3 and 4 show the effect of multi-color colony segmentation using the fast multi-color classification technique.
Figure 3 shows the automatic classification test for three color colonies. First, the prior knowledge of the three colonies of red, blue and yellow was obtained from the colony image (Fig. 3-a), and added to the constraints of the CV level set active contour model by the RGB model. Thus, in the evolution of the CV model, only the specified color contours are shrunk, and the classification results are shown in Figure 3-b.

Figure 3 Automatic classification effect of multi-color colonies
Figure 4 shows an automatic classification of multicolor colonies containing two color colonies but with significant pigment diffusion. The method is the same as above, firstly obtain the prior knowledge of the red and green colonies from the colony image (Fig. 4-a), and add it to the constraint condition of the CV level set active contour model through the RGB model. Thus, in the evolution of the CV model, only the specified color contours are shrunk, and the classification results are shown in Figure 4-b.
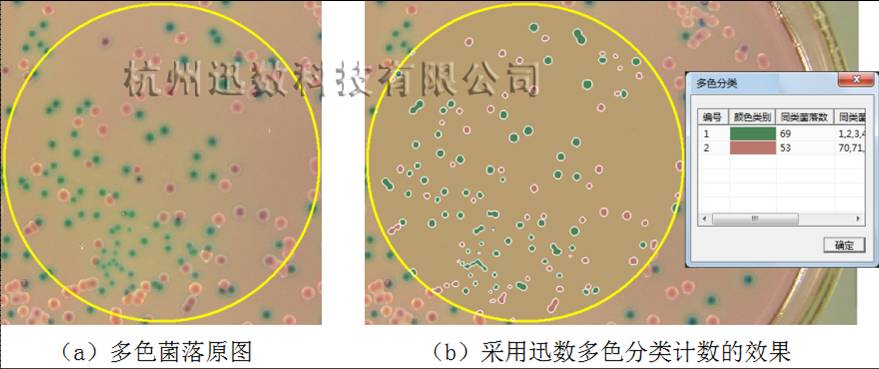
Figure 4 Automatic classification effect of multi-color colonies
3 , summary
The image segmentation method based on the horizontal set active contour model has the advantages of strong anti-noise performance, good numerical solution stability, smooth and continuous segmentation boundary, and can handle complex topology. It can solve many complicated problems.
After more than two years of research, the Xun Science and Technology R&D team not only mastered this advanced technology, but also introduced various constraint mechanisms and boundary conditions based on the characteristics of microbial colonies based on the traditional level set active contour model. Creative research has developed advanced image segmentation or automatic classification techniques for a variety of complex situations, providing practical and advanced techniques for colony counting and microscopic image analysis.
Hangzhou Xunda Technology Co., Ltd. R & D Department JIANGSU CLS TECHNOLOGY CORP.LTD , https://www.js-cls.com