Research on particle sphericity detection technology
Ren Zhongjing
Jinan University Institute of Particle Testing  Jinan, Shandong 250022, China
Abstract: In this article describes a laser DU by sedimentation analysis and comparison of the data analysis method DU large spherical degree, gives an application example, and made concise analysis principle.
Key words : sphericity ; grain shape ; particle size analysis ; measurement ; laser
Particle sphericity is one of the basic parameters of the particle. The size of the sphericity directly affects the fluidity and packing properties of the particles. At present, the detection of sphericity mainly depends on the microscope. The main disadvantage of this method is to detect slow, but belongs to two-dimensional detector. It is difficult to distinguish the sphericity of the flaky particles from the difference in the sphere. Therefore, it is necessary to develop a new sphericity detection method.
1, the principle
1.1 definition
Previously, particle sphericity was defined as the ratio of the equivalent diameter of the perimeter of the particle to the equivalent diameter of the particle area. The secondary definition is actually limited to a two-dimensional description, and it becomes more appropriate to become circular. He cannot accurately characterize the shape of three-dimensional particles. The sphericity of a three-dimensional particle can be defined as the ratio of the surface area equivalent diameter of the particle to the volume equivalent diameter of the particle.
Q=d s /d v
Where d s represents the equivalent surface area of ​​the particle, and the surface area of ​​the particle is S , then S = πd 2 s

Test method and data analysis According to formula (5) , as long as the sedimentation particle size and laser diffraction particle size of the particle group are measured, the sphericity can be calculated. Further, any method for measuring the particle size distribution of the particles can obtain a series of characteristic particle diameters such as d . (i= 0,1, 2 Â ... 10) corresponding to the diameter of the particle generation feature (5), the distribution function to obtain the sphericity of the particles. This function can meticulously describe how the sphericity of the particle group varies with the particle size. Figure 1 shows the cumulative distribution of particle size distribution for a set of particles, with the abscissa being the particle size number. It can be seen from Fig. 1 that the sedimentation particle size analyzer measures less than the laser particle size analyzer. This indicates that the particle group is certainly not spherical.
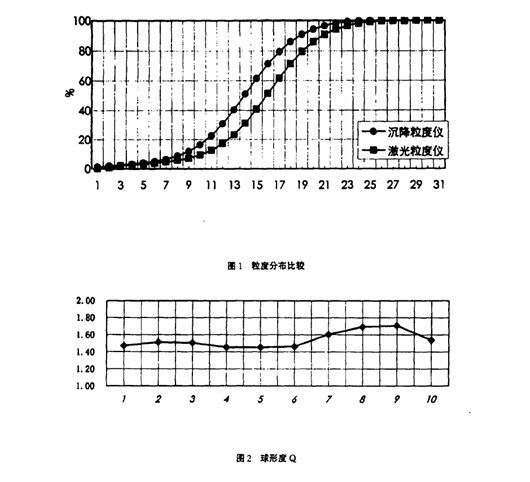
Table 1 is the characteristic particle diameter calculated from the data of Fig. 1 and the sphericity calculated according to the formula (5) .
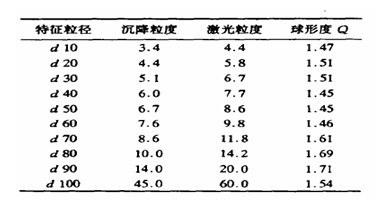
Figure 2 depicts the distribution of the sphericity of the particles as a function of particle size. The abscissa d 10 represents d 20 and so on. It can be seen from the graph that the particle sphericity of the sample does not change much with the particle size. The sphericity is between 1.4 and 1.7 .
3 summary
In this paper, the expression of the three-dimensional sphericity of particles is theoretically derived. The authors used the method of sedimentation method to compare the particle size of the corresponding particle size in the laser diffraction method to determine the sphericity of the particles. It solves the problem of accurate measurement of particle sphericity creatively , and has the characteristics of clear concept, simple and practical. Has a promotional value.
references
[1]Allen T, Particle Size Measurement (4th)[M],
[2] according to any Chukyo. Graphite powder shape parameters of the distribution [J], China Powder Science and Technology, 1999.5 (2) 19-21
[3] Ren Zhongjing . Non-spherical particle elliptical diffraction model for laser particle size analysis [J] .China Laser ,1997.24(2)
YT-S350
YT-S350
Shenzhen Sunshine Technology Co.,Ltd , https://www.szyatwin.com