Today, I would like to tell you about a fund project, the division of walnut inefficient forest types and their transformation techniques in Chengdu. Farmers who have ideas about the walnut planting industry can learn more about the experience of other regions.

1 walnut low-efficiency forest, type division and its standard
Low-efficiency forests generally refer to fruit trees that yield lower yields than a certain age group. According to the forestry standard (LY/T1329-1999), the high yield and quality of walnuts are as follows.
Table 1 Early walnut low-yield garden standard
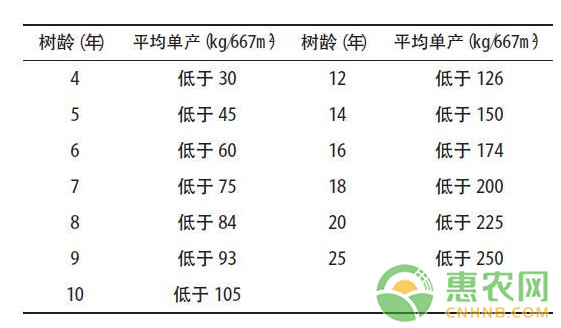
According to the low yield of forest stands, the low-yield walnut forests are classified into Class I, Class II and Class III forests. The division criteria are as follows.
Class forest: The excellent variety is more than 60%, the tending tube is poorly protected, and the pests and diseases are serious. Class II forest: The excellent variety is below 60%, and most of the plants are in the middle and young forests (the tree age is less than 15 years), and the growth is robust. Class III forest: The excellent variety is below 60%, and the old, weak and diseased plants account for more than 2/3 of the total forest.
2 Transformation technology
The transformation technology is classified according to three different types of walnut low-yield forests, namely, tending transformation (class I forest), high replacement (class II forest), and upgrading (class III forest).
2.1 Tending and Reforming (Class I Forest)
2.1.1 Stand density adjustment. Excessive forests are divided into old, inferior, diseased plants and poor quality plants, and the number of suitable plants (the canopy is not covered) is evenly distributed. The canopy closure is adjusted at around 0.8.
2.1.2 Replanting of open space. For the low-yield forest open space of walnuts (the original open space, planting dead and cutting off the old and inferior disease plants with a spacing of more than 12m × 12m), the grafting seedlings with the same age and flowering period are used for replanting. Take a large hole (100cm × 100cm × 80cm) to prepare the ground, and apply enough base fertilizer (organic fertilizer) in the hole. The replanting season is suitable for early spring. When planting, roots, seedlings, and soil fill the soil.
2.1.3 Renovation of soil. For low-yielding forests with poor site conditions, the weeds in the vertical projection range of the canopy can be cut off in winter or spring. It can be combined with organic fertilizer, deep-turning the soil more than 30cm, shallow inside and outside, picking up the grass roots in the tree tray, Stones, and flatten the soil in the tree tray; weeding the soil in summer, and the thickness of the tree is 20~25cm.
2.1.4 Water and fertilizer management. (1) Base fertilizer: It is mainly based on organic fertilizer, and is applied before fruit harvesting and before falling to the leaves. According to the size of the tree, 10~20kg/strain of young trees, 20~50kg/plant of first fruit, and 50~100kg/plant of fruit during fruiting. Fertilization method: The saplings are applied around the trunk along the outer edge of the canopy and dug 20 cm wide. The first fruit stage tree and the fruit-bearing period tree are applied 2/3 in the outer periphery of the canopy and 1/3 outward, and 4~8 radial grooves of 30cm in width and 40~50cm in depth are applied. The applied fertilizer should not adversely affect the orchard environment and fruit quality. (2) Topdressing: Take the trunk as the center, from the 1/2 of the crown diameter to the edge of the crown, and dig a few fertilization points with a length and width of 20cm × 20cm and a depth of 10~15cm. Top dressing before germination: combined with irrigation, mainly nitrogen fertilizer; saplings applied urea 100~200g, the initial 300~500g, the result is 500~800g. Topdressing during fruit development: in the middle and late May, nitrogen is the main source, supplemented by phosphorus and potassium. The saplings are applied with urea 50~100g, superphosphate 100~150g and potassium chloride 30~50g. Results: initial application of urea 80~100g, superphosphate 150~200g, potassium chloride 50~100g; Apply urea 100~150g, superphosphate 200~250g, and potassium chloride 100~150g. Topdressing during nucleolar development: in early July, mainly phosphorus and potassium fertilizers. The saplings are applied with 200-300 g of calcium phosphate and 50-100 g of potassium chloride. Adult trees are subjected to 300-500 g of calcium phosphate and 100-200 g of potassium chloride. Results The initial plant was applied with 300-350 g of calcium phosphate and 100-150 g of potassium chloride. As a result, the plant was applied with 350-450 g of calcium phosphate and 150-200 g of potassium chloride. (3) Irrigation: Irrigation 2~4 times a year. In the arid area of ​​Longquan Mountain, dig 2~4 deep and 40cm diameter holes around the tree tray, fill the holes with weeds or crop straws, then apply appropriate amount of compound fertilizer, fill the water, dry the soil with fine soil Cover and cover with mulch film. Irrigation period: before germination, it can be combined with fertilization; in May, the fruit is swollen in the rapid expansion period; after harvesting, the fruit is combined with the autumn application of base fertilizer; the soil is frozen before freezing.
2.1.5 Plastic trimming. Adapted to local conditions, trimmed by trees, and shaped with trees. The main method of tree crown structure adjustment is to adjust the tree shape, and cultivate the trees with obvious branches in the center to form an evacuated layered shape. If the center leader branch is too weak or the center leader branch is not obvious, it will be cultivated into a natural happy shape; Squeezed, overlapping, crossed branches and diseased branches, dry branches; retracted peripheral weak or long branches; medium and short branches within the canopy, without short cuts, to promote the formation of the resulting mother branches. The long branches and the erect branches are appropriately short-cut, and the branches are promoted to form branches; the aging branches are updated and trimmed. Trimming time: After harvesting in autumn and before falling leaves.
2.1.6 Flower and fruit management. (1) De-male: The result is a large tree, which is 90% to 95% of the amount of male flowers when the male flowers begin to expand. (2) Fruit thinning: For varieties with high fruit set rate and weak trees with more fruit, the fruit is thinned after the physiological fruit drop period, and 60~80 fruits are retained per 1m2 crown.
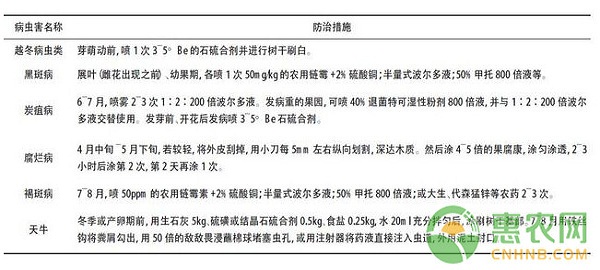
2.1.7 Pest control. Pest control methods mainly include forestry technology control, physical control and chemical control. Among them, forestry technology control and physical control are the mainstays, supplemented by chemical control. When pests and diseases occur, forestry technical control and physical control measures are preferred, and chemical pesticides are used when necessary. Pesticides are prohibited for 60 days before harvesting. The use of pesticides should comply with the provisions of NY/T1276 and GB4285. See Table 2 for the main pest and disease control methods. Try to use safe, high-efficiency and low-residue pesticides. It is strictly forbidden to use “three high†pesticides.
Prevention and control of forestry technology: (1) After harvesting, the walnut forest will be trimmed and trimmed, and the forest and the tree body will be kept ventilated and light-transmitted, and the pests and branches will be removed to reduce the occurrence of pests and diseases. (2) The winter recovery will help the prevention and control of pests and diseases. (3) After harvesting, thoroughly clean the litter, diseased fruit and weeds in the orchard before germination, and burn it intensively. (4) Apply organic fertilizer in time after harvesting to improve the ability of plants to resist pests and diseases.
Physical control: (1) Use insect-loving food as a bait to lure. (2) Install 1~2 ç› frequency vibrating insecticidal lamps every 5hm2 to kill adult worms.
Table 2 Main pest control
2.2 High-replacement (Class II forest)
2.2.1 Rootstock selection. The stem has a trunk diameter of less than 5 cm and is grafted with a trunk. The dry diameter is more than 5cm, and each plant chooses 3~4 branches with the branch angle, height, smoothness and no pests and diseases as the rootstock branches.
2.2.2 Variety selection. Choose the varieties that have been tested at the provincial level and above, and that have performed well in the local area, with high yield and high quality, or those that have performed well through the introduction test. It is mainly characterized by Sichuan early, double early, medium-nuclear short branches, Liao nuclear, and thin shell incense.
2.2.3 Collection and storage of scions. The collection time is collected before the beginning of winter or spring. The upper part of the sapling canopy is enriched, robust, full of axillary buds, free from pests and diseases, and the vegetative shoots are 1.0~1.5cm in thickness. Combine plastic trimming to leave 2~4 buds at the base of the branches or to cut from the base. After the scion is harvested, each 30 or 50 is bundled to indicate the variety, time, location and quantity. The local scion should be followed by the pick. Externally adjust the scion Moisturizing transport, store in a cool and humid place, or store at 0~4 °C.
2.2.4 Grafting period. During the leaf-expansion period, it is generally from the end of March to the end of April. It is better to peel off the bark at a specific time.
2.2.5 Grafting method. Use the tongue and tongue connection method. The rootstock is drained, the anvil is cut, the anvil is cut, the ear is cut, the anvil is cut, and the lashing is carried out in 6 steps. Specific operations: (1) Water for rootstock: 2 weeks before grafting, saw 1~2 spiral saws from the ground 20~30cm or cut 2~3 knives with a knife to reach the xylem. (2) Broken anvil: Select a smooth part for cutting (branches), trunk grafting, 0.5~0.8m cutting. (3) Anvil cutting: The kerf is flattened with a grafting knife, and the surface of the noodles is slightly sloped. (4) Crushing: Cut the scion into 10~15cm, with 2~3 buds, keep 1~2 full buds in the upper part, and cut the lower end into 12~15cm horse-shaped cut surface, smooth noodles, front cut Thin tongue. (5) Cutting the cuttings of the anvil: cutting the crescent-shaped incision of 2~4cm in the smooth part of the broken anvil, and then cutting off some of the thick old bark from the bottom to the crescent-shaped incision along the trunk (branch), revealing that the tender skin is about thick 2~3mm, the noodles are horse-shaped, about 20cm long, 1~2cm longer than the scion. The skin layer at the front end of the cut horse-shaped cutting strip is gently peeled off the xylem, and the xylem of the scion is inserted into the formed layer of the cut crescent-shaped incision, which is between the skin and the xylem, and the outer skin of the scion is just covered. On the tender skin of the horse-shaped noodles of the rootstock, the insertion depth is close to the scion of the scion and the crescent-shaped cut surface of the rootstock, and the core of the scion can be pressed. (6) Binding: Use a plastic film tape with good elasticity, strong pulling force and width of 1.5cm to bind the scion from bottom to top and tighten when tying.
2.2.6 Management after connection. Mainly include: (1) Tree expansion tray: The tree trunk is centered on the trunk, and the tree tray with a radius of 1m is expanded outwards. (2) Wipe: Remove the sprout on the rootstock in time. (3) Windbreak: When the new shoot grows to about 50cm, tie 2~3 pillars of suitable length on the trunk (branches), gently tie the new shoots on the pillars to prevent wind folding, and tie with the growth of new shoots. 2~3 times. (4) Loose binding: Remove the binding material at the interface about 3 months after grafting. (5) Thinning and shaping: If there is a female flower after grafting and grafting, it should be thinned out early. Timely evacuation of branches that are too dense, intersecting, overlapping, drooping, thin, and improperly placed, and shaped with the tree.
2.2.7 Water, fertilizer management and pest control. Refer to 2.1.6 and 2.1.7.
2.3 Renovation (Class III Forest)
2.3.1 Variety selection. Refer to 2.2.2.
2.3.2 Forest land clearing. Manually cut and clean the existing walnut forest.
2.3.3 Site preparation. According to the plant spacing (4~5m) × (4~6m), the grounding was done in the same way. Dig a hole 100cm × 100cm × 80cm.
2.3.4 Applying base fertilizer. 20~25kg of simmered manure in each planting hole, mixed with topsoil. Backfill the soil to 30cm from the ground.
2.3.5 Seedling quality requirements. Grafted seedlings with strong stout, high degree of lignification, developed root system, short main root, good healing of grafting interface, no pests and diseases and mechanical damage were selected.
2.3.6 Planting. The steps are as follows: (1) Planting time: autumn planting or spring planting. Autumn planting, after the leaves of the seedlings are frozen until the soil is frozen; spring planting, after the soil is thawed, before the seedlings sprout. (2) Treatment of seedlings before planting: Before planting, the main roots of the seedlings and the thicker lateral roots are lightly cut into a slope, and the injured roots are cut off. (3) Planting: Put the seedlings in the right place, set the roots well, backfill the fine soil, step on the soil; plant the deep root neck soil marks and the ground level; water the water, water seepage, then return to the fine soil, make a tree plate, cover The membrane is compacted around it. (4) Ding dry: After planting, the dry height is 0.5~0.8m, and the strong bud is left under the cut, and the cut is about 1.0cm away from the bud. If the dry height is not reached, the drying will not be carried out, and the top buds of the seedlings will grow upright to form thicker branches. When the height is fixed, the plastic belt will be short-cut.
2.3.7 Post-plant management. Mainly include: (1) Wiping: Leave a plastic band of 30~40cm under the cut, and wipe all the buds under the plastic band. (2) Elimination of male and female flowers and young fruit: timely removal of male and female flowers and young fruit within 3 years after planting. (3) Intercropping: Before planting, before the crown is handed over, the inter-row will be a short-bar economic crop, pasture, green manure or Chinese herbal medicine. (4) Shallow soil turning: At the end of autumn and winter, the trunk is the center, the radius of the canopy is 50cm, and the depth is 20~30cm. (5) cultivating and weeding: 2~3 times in the growing season and about 10cm in depth and weeding. (6) The trunk is white: the trunk is white before winter.
2.3.8 Young tree shaping and pruning. (1) Natural happy shape shaping process: 3~4 branches or germinated buds are left as main branches in different directions in the plastic code band. The vertical distance of the base of each main branch is generally 20~30cm, and each adjacent branch The horizontal distance (or angle) should be consistent or close, and the growth potential is consistent. After the main branch is selected, the first-level side branch is selected. Each main branch can be left with 3 left and right side branches, which are staggered up and down, left and right, and distributed evenly. The distance of the first side branch from the trunk is 0.6~0.8m. After the primary side branch is selected, in the larger happy tree body, the secondary side branch can be selected on it. The number of secondary side branches on the first-stage side branches was 2-3, and the resulting branch group was cultivated thereon. (2) Evacuation and stratification process: 1 cultivation of the stem of the tree center. In the plastic belt, the first erect new shoot is selected for the center. When reaching the height of the main branch culture of the second layer (1.2~1.5m from the main branch of the first layer), the center is short-cut, which causes the branch to form the second branch. When reaching the height of the third-layer main branch culture (0.5~0.6m from the main branch of the second layer), the center is again short-cut, and the branches are formed to form the third-layer main branch. When the third layer of main branches is formed, the center stem can no longer be cultured. 2 main branch culture. Select the main branch in time in the plastic belt. The main branches of the first layer are generally three, and the positive branches should be selected, and the vigorously growing branches should be cultured. The horizontal angle of the three main branches is about 120°, and the angle between the three main branches is about 60°, and the distance between the three main branches is 40~50cm. After the main layer of the first layer is selected for 2~3 years, the main branch of the second layer can be selected, the layer spacing is 1.2~1.5m, and the number is 2~3. The 3rd main branch is selected after 6~7 years after planting, and the distance between the layers of the 2nd layer can be appropriately smaller. 3 side branch culture. Generally, 3~5 side branches are selected on the main branch of the first layer, 2~3 side branches are selected on the main branch of the second layer, and 2 side branches are selected on the main branch of the third layer. When the side branch is selected, the distance between the side branch and the trunk should be 40~60cm, and the side branch of the same level is in the same side direction of the main branch. The position between the lateral branches on the same main branch should be appropriate, and the second lateral branch should be selected on the opposite side of the first lateral branch. 4 groups were cultured. The middle and short branches of each part of the canopy are not short-cut, which promotes the formation of the resulting female branches. Long branches and erect branches are appropriately short-cut to promote branching to form branches.
The above is all the content of today, I hope that the farmers can help, and more agricultural technology skills in the Hui Nong network!
Sleep improvement/Anti-anxiety
We're well-known as one of the leading Health care supplement--Sleep improvement/Anti-anxiety manufacturers and suppliers for our quality products and good service. Please feel free to buy or wholesale bulk 5-htp Griffonia Seed Powder, L-Theanine powder, Valeriana Officinalis Acid Root Extract Powder, Apigenin and nicotinamide mononucleotide 99% nmn powder for sale at the best price from our factory.
Anti-Anxiety Plant Extract,Sleep Improvement Powder,Sleep Improvement Extract,Sleep Improvement
Xi'an Natural Field Bio-Technique Co., Ltd. , https://www.naturalnf.com