
The carbon dioxide incubator simulates the formation of a cell/tissue-like growth environment in the organism by incubating in an incubator, such as a stable temperature (37 ° C), a stable CO 2 level (5%), and a constant pH (pH: 7.2-7.4), a higher relative saturation humidity (95%), a device for in vitro culture of cells/tissues.
Application range
It is widely used in cell, tissue culture and culture of certain special microorganisms, and is commonly used in cell dynamics research, collection of mammalian cell secretions, carcinogenic or toxicological effects of various physical and chemical factors, research and production of antigens, Culture of hybridoma cells to produce antibodies, in vitro fertilization (IVF), stem cells, tissue engineering, drug screening and other research fields.
User request
Users have two basic requirements for carbon dioxide incubators:
First, the carbon dioxide incubator is required to provide the most accurate and stable control of temperature and carbon dioxide concentration, so as to facilitate the progress of its research work;
Second, the carbon dioxide incubator is required to effectively prevent microbial contamination in the incubator, and to eliminate pollution regularly to protect research results and prevent sample loss.
Microprocessing control system
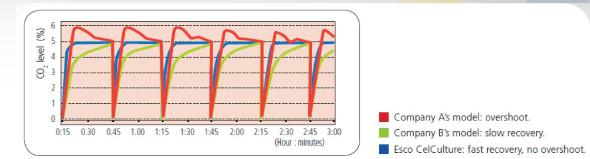
The microprocessor control system is an operating system that maintains the steady state temperature, humidity, and CO2 concentration in the incubator. The use of micro-processing control systems and various other functional accessories (such as high and low temperature automatic adjustment and alarm devices, CO2 alarm devices, password protection settings, etc.) makes the operation and control of the CO2 incubator very simple.
Such as: PID microprocessor touch screen control system with LCD screen display, it can strictly control the concentration of gas and reduce its loss to an extremely low level, to ensure a constant culture environment, and to ensure the box during long-term cultivation. Accurate internal temperature, liquid crystal display, can achieve graphical process monitoring, intervention event recording and so on. In addition, the alarm system is also indispensable. It allows you to know the situation of the incubator and react in time to minimize the loss and ensure the continuity of the experiment. Some incubators have sound/light alarm devices. When the temperature changes by ±0.5°C, or the CO2 concentration changes by ±5%, it will automatically alarm; some have the CO2 concentration abnormal alarm display function; some have low voltage and power failure alarm functions. These devices are designed to be user-friendly and reduce the tedious and tedious experimental process.
heating method
Both air jacketed and water jacketed, both heating systems are accurate and reliable, and they all have their own advantages and disadvantages.
Water jacket heating maintains a constant temperature by enclosing an internal tank through a separate water jacket. The advantage is that water is a good thermal insulation material. When a power failure occurs, the water jacket system can Keeping the temperature accuracy and stability in the incubator for a long time is beneficial to users who are not stable in the experimental environment (such as useful power limitation or frequent power outage).
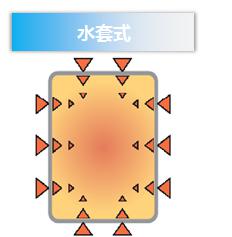
The gas-sleeve heating is to directly heat the inner tank through the heaters in the gas jacket of the tank, and is also called direct heating on six sides. Compared with the water jacket type, the gas-sleeve type has the characteristics of quick heating and rapid recovery of the temperature than the water-type incubator, which is particularly advantageous for short-term cultivation and the need for frequent switching of the box door. In addition, the air-sleeve design is simpler for the user than the water jacket type (the water jacket type needs to add water, empty and clean the water tank, and often monitor the operation of the water tank, as well as potential pollution hazards).
Carbon dioxide concentration control
The carbon dioxide concentration can be measured by an infrared sensor (IR) or a thermal conductivity sensor (TC). Both sensors have their own advantages and disadvantages.
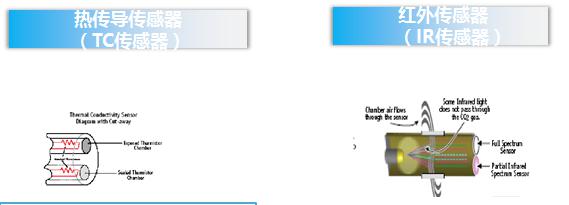
The working principle of the thermal conductivity sensor to monitor the CO2 concentration is based on the continuous measurement of the thermal conductivity of the internal cavity air. The low thermal conductivity of the input CO2 gas changes the thermal conductivity of the air in the cavity, thus producing a direct concentration with the CO2 concentration. A proportional electrical signal.
One disadvantage of the TC control system is that changes in temperature and relative humidity within the chamber can affect the accuracy of the sensor. When the door is frequently opened, not only the CO2 concentration, temperature and relative humidity will fluctuate greatly, thus affecting the accuracy of the TC sensor. This control system is less suitable when precise culture conditions are required and the incubator door is frequently opened.
Infrared sensor (IR) It uses an optical sensor to detect CO2 levels. The IR system includes an infrared emitter and a sensor. When the CO2 in the tank absorbs part of the infrared light emitted by the emitter, the sensor can detect the amount of infrared radiation, and the amount of absorbed infrared light corresponds to the level of CO2 in the tank. Thus, the concentration of CO2 in the tank can be obtained.
Relative humidity
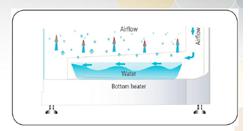
The humidity inside the box is a very important but often overlooked factor for the training work. Maintaining sufficient humidity levels and having a fast enough humidity recovery rate (such as after opening and closing the door) will ensure that the culture fails without excessive drying.
At present, most carbon dioxide incubators generate moisture through the evaporation of the humidification disk (the relative humidity level is about 95%, but the humidity recovery rate is very slow after opening the door). Try to choose an incubator with a large humidity evaporation area, because the larger the humidity evaporation area, the easier it is to reach the maximum relative saturation humidity and the shorter the recovery time after the door is opened and closed.
Contaminant control
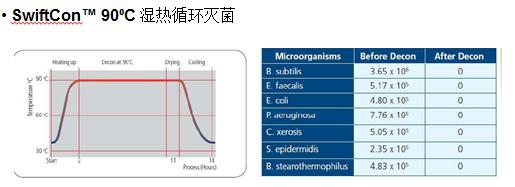
The 90 °C moist heat sterilization cycle of the CO2 incubator was evaluated by the British Health Protection Institute (HPA) and proved to be an effective method for inactivating fungi, bacterial spores and vegetative cells.
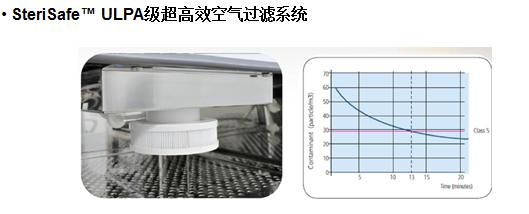
Contamination is a major cause of cell culture failure. Manufacturers of carbon dioxide incubators have designed a variety of different devices to reduce and prevent the occurrence of pollution, the main way is to minimize the areas and surfaces that microorganisms can grow, and combine Automatically eliminate contaminated devices to effectively prevent pollution.
For example, in view of the fact that CO2 incubators are sometimes accompanied by mold growth during use, some companies have developed CO2 incubators with UV disinfection to ensure that the incubator is protected from contamination and to ensure biocleanability in the instrument case; The company designed ULPA high-efficiency filter to filter the air in the incubator, which can remove 99.97% of particles above 0.3um. In addition, the 900C moist heat sterilization device can kill all contaminated microorganisms in the box, even high temperature resistant microorganisms such as spores. It is more secure for cell culture.
Precautions for use
1. The instrument should be placed on a flat surface, the environment should be clean and tidy, dry and ventilated;
2. Do not adjust the inflow gas pressure too large to avoid breaking through the pipeline;
3. Periodically (at least every two weeks), replace sterile distilled water or sterile deionized water in the water tray.
4. At least 3 people need to know the operation password setting, so as not to forget the password and can not open the instrument;
5. Keep the air in the incubator clean and disinfect regularly;
6. Always pay attention to the amount of distilled water in the distillation tank in the tank to maintain the relative humidity inside the tank while avoiding evaporation of the culture solution;
7. Not applicable to the cultivation of articles containing volatile chemical solvents, low concentrations of explosive gases and low ignition gases, and the cultivation of toxic substances;
8. Proper use and attention to the maintenance of the instrument, so that it is in good working condition, can extend the life of the instrument;
9. If the CO2 incubator is not used for a long time, the moisture in the workroom must be removed before closing. Open the glass door and ventilate for 24 hours before closing.
10. The carbon dioxide incubator should not be inverted, and the door should not be lifted to avoid deformation of the door.
Analytical Instrument,Soil Nutrient Tester,Nitrogen Soil Tester,Digital Nitrogen Soil Tester
Guangdong Widinlsa International Co.Ltd , https://www.guangdongwidinlsa.com