Introduction
Western blot is one of the commonly used protein detection methods in biological laboratories. It has been in existence for several decades since its introduction in 1979. Used to analyze the expression of proteins. Target proteins are detected by specific binding of antigen-antibodies, and commonly used detection methods include chemiluminescence and fluorescence. The fluorescence detection method is more and more popular because of its ability to perform multiple detections and signal stabilization. The secondary antibody directly labels the fluorescent group, and the fluorescence signal intensity is proportional to the target protein concentration, and does not depend on the enzymatic reaction, and the quantification is more accurate. NIR near-infrared fluorescence detection method, the autofluorescence of the imprinted membrane is low, and the signal-to-noise ratio is high. NIR fluorescence detection for high signal-to-noise ratio and high quality images relies heavily on high excitation intensity, precision laser sources and professional optics.
Laser light source is easier to reach the absorption peak of dye than LED, xenon lamp / halogen lamp
In imaging systems, the choice of source is based on its ability to excite specific dyes. The criterion for selecting a source is to find an available excitation light that can deliver the necessary energy (the light that actually excites the fluorescent probe) while minimizing wasted wavelength light waste. Standard. The biggest advantage of laser source near-infrared imaging is that it is closer to the excitation peak of ordinary dyes.
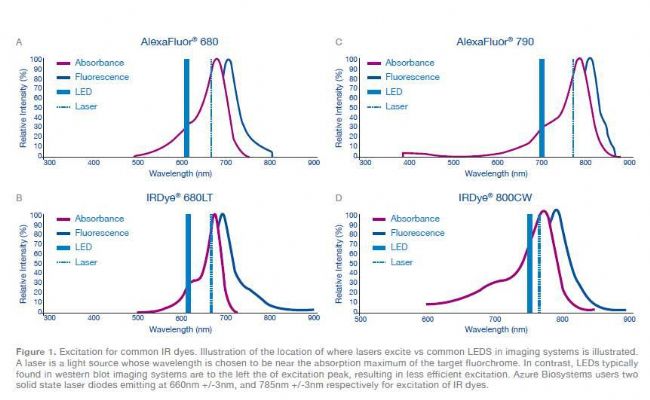
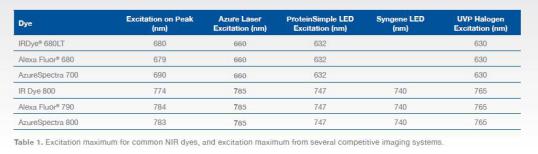
For example, the dyes IR Dye® 700 and Alexa Fluor® 680 have a maximum absorption peak at 685 nm (Figure 1A, 1B, and Table 1). The Azure Biosystems cSeries imaging system has a 660 nm laser source with LED or white light (xenon and halogen) The excitation source of the lamp is around 630 nm, and the dye excitation is incomplete.
The dyes IR800 and Alexa Flour have a maximum absorption peak at 780 nm (Fig. 1C, D and Table 1). The Azure Biosystems cSeries features a 785m laser source. The excitation light using LED or white light (xenon lamp and halogen lamp) is in the left direction of the maximum absorption peak, and the dye excitation is incomplete.
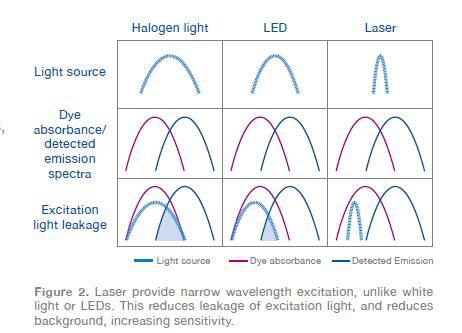
Narrow-spectrum lasers reduce the generation of light leakage
The laser provides a powerful, accurate excitation within the excitation peak of the selected dye. Narrow-spectrum excitation eliminates light leakage and artifacts compared to weak, non-specific LED and xenon/halogen white light source systems (Figure 2). Reduce image noise and improve signal to noise ratio.
Laser detection achieves higher sensitivity in less time
The laser source is connected to the maximum absorption peak of the NIR dye and provides less light leakage. So how does it affect imaging? The gradient-loaded blotting membrane was incubated with goat anti-rabbit IR 700-labeled antibody. The blotting membrane was first exposed for 30 s using an LED imaging system and then exposed for 10 s using a laser imaging system (Fig. 3A). Even if the imaging time is 3 times less, the same number of bands can be seen on the blotting film. The laser source is closer to the absorption peak of the dye, helping the user to save imaging time.

Laser detection has a lower background
The good or bad signal-to-noise ratio of the data is part of it, not entirely determined by the signal strength. Saving time is one of the benefits, and the second benefit is that shorter exposure times help reduce background fluorescence. The signal-to-noise ratio is obtained by analyzing the signal strength of each bright strip divided by the background intensity of the selected area (Figure 3). Short imaging time can reduce background, improve signal-to-noise ratio and have better sensitivity.
to sum up
The laser source is closer to the maximum absorption peak of the NIR dye, and the excitation intensity is large with less light leakage. Short imaging time, low autofluorescence and high signal-to-noise ratio.
The Azure C600 imaging system is the only imaging system on the market that can perform laser near-infrared, chemiluminescence, and multi-color fluorescent western blotting analysis to meet the various imaging needs of the laboratory.
The Azure C150 and C200 are basic models that can be upgraded from the C200 to the c300, c400, c500 and c600 models. Therefore, there is no need to replace the instrument to achieve the functions of UV, visible light, chemiluminescence, multi-color fluorescence and near-infrared imaging.
references
1. Towbin, H., Staehelin, T., & Gordon, J. (1979). Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. PNAS, 76(9), 4350–4354.
2. http:// LEDs_LaserAdvantage_no2_Spectral_Brightness.pdf
Due to the irregular characteristics of the pelvic structure, the choice of internal fixation is diverse.
For patients separated symphysis pubis, a 2 or 4 holes, 4.5 or 3.5mm diameter dynamic compression plate or reconstruction plate can be used and fixed with full-thread cancellous bone screws.Another method of fixation is lag screw fixation. In patients with new sacroiliac joint dislocation with a forward approach,firm fixation can be achieved by using 2holes 3.5mm dynamic compression plates through the front of the sacroiliac joint. The posterior approach can also be used to insert 6.5mm lag screws into the sacral wings or hollow cancellous bone screws with interosseous compression for firm internal fixation. If available, the fracture may be fixed with 3.5mm or 4.5mm pelvic reconstruction plates and appropriate full-thread cancellous bone screws.
Pelvic Plate,pelvic fracture treatment,pelvic fracture,pelvis plate
Jiangsu Aomed Ortho Medical Technology Co.,Ltd , https://www.aomedortho.com